-40%
Bard Infection Control Urine Drainage Bag With Anti-Reflux Chamber 2000 ml
$ 5.33
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
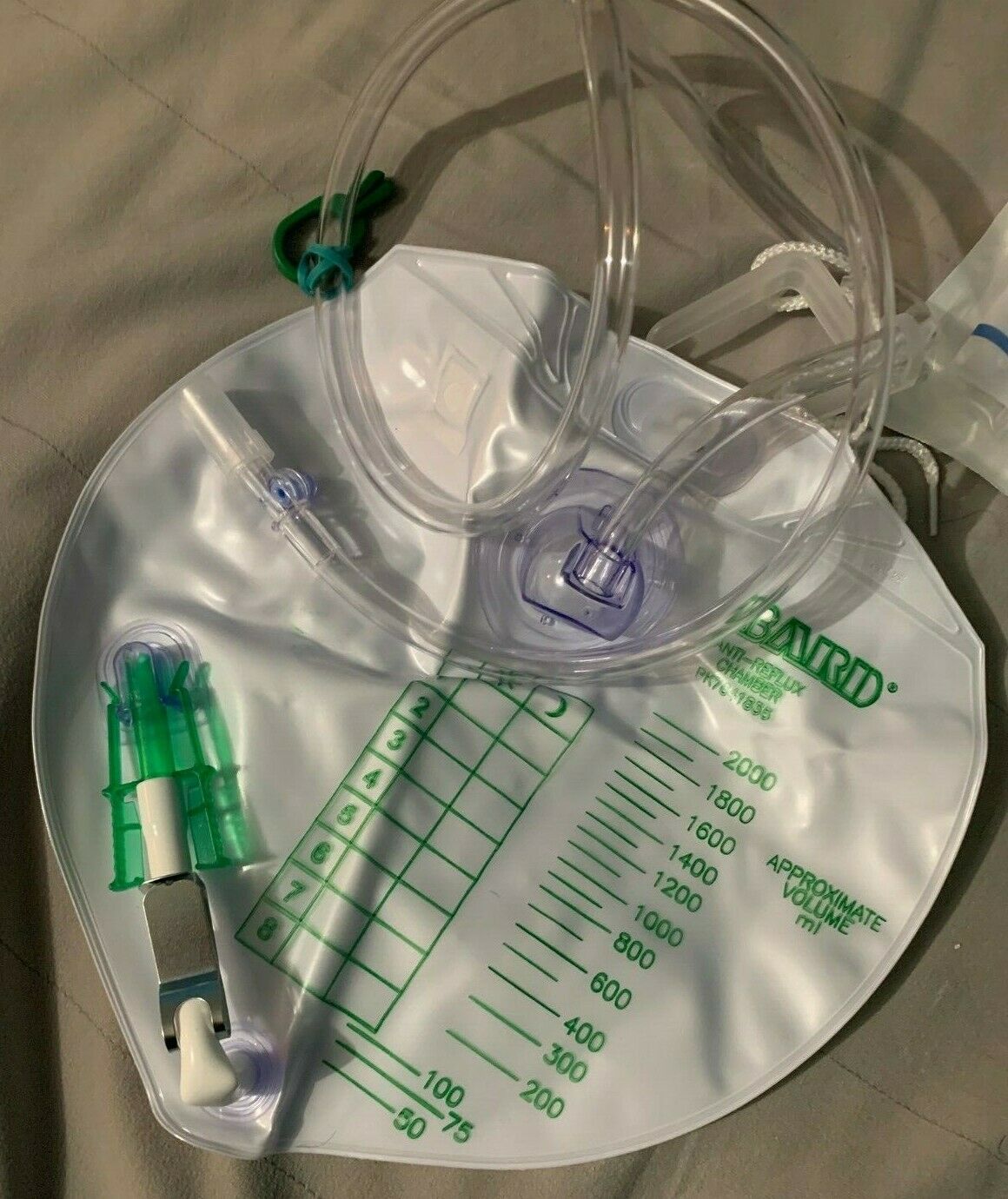
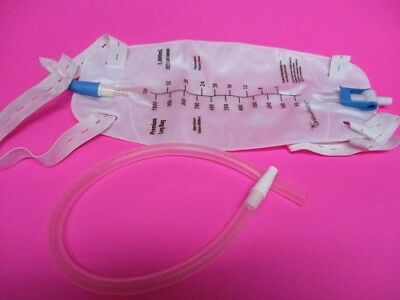
Bard Infection Control Urine Drainage Bag With Anti-Reflux Chamber features a rounded, teardrop shape that ensures more efficient drainage. Microbicidal Outlet Tube protects the drain bag from contamination resulting from retrograde bacterial migration. Bard EZ-Lok sampling port eliminates the risk of needlestick injuries and allows for needle-free aspiration.Features of Bard Urinary Drainage Bag with Anti-Reflux Chamber
·
Unique dome design of the anti-reflux chamber prevents urine reflux from the urine drain bag back into the drainage tube
·
2000 ml drainage bag
·
Single-use
·
Sterile
·
Latex free
·
NO
needles
·
How to use Infection Control Urinary Bag?
o
Hold spine and lift meter to facilitate emptying.
o
Periodic inspection of the system should be made to ensure that urine is flowing freely and is not obstructed.
o
Bard
urine drainage bag should be placed near the foot of the bed, and below the level of the patient hip.
o
Drain tubing should be secured to the draw sheet with the sheeting clip to provide a continuous downward sloping path to the drainage bag.
o
When transporting the patient, do not place the drainage bag on the patient abdomen or between the legs.
o
Excess tubing should be arranged to permit "straight line" drainage or coiled in a manner that does not allow the tubing to kink or fall below the level of the drainage bag.
o
To promote optimum drainage, position the drainage tubing over the patient leg. This is especially important if the patient is obese.
o
Never allow the drainage bag to be placed on the floor.
·
Precautions to take While using Bard Drainage Bag
1.
Always keep the drainage bag lower than the catheter and the patient’s bladder:
§
When the patient is being transported on a gurney
§
When the patient ambulates
§
When the patient is using a wheelchair
2.
Always arrange tubing in a straight-line fashion.
§
Position tubing over patient’s leg
§
Secure tubing to sheets using sheet clips
3.
Avoid compromising the closed system of the drainage bag. Many urine drainage problems can be solved by:
§
Repositioning the patient, drainage bag or tubing
§
Confirming that the Foley catheter is fully inserted into the bladder and fully inflated with the accurate volume of sterile water based on the recommended inflation volume
4.
Wash your hands immediately before and after any manipulation of the catheter site or apparatus
5.
Obtain specimens from a needleless safe sampling port using aseptic techniques
6.
Always use a separate collection container for each patient when draining